Installing the Bareos Server
If you are like me, you want to get Bareos running immediately to get a feel for it, then later you want to go back and read about all the details. This chapter attempts to accomplish just that: get you going quickly without all the details.
Bareos comes prepackaged for a number of Linux distributions. So the easiest way to get to a running Bareos installation, is to use a platform where prepacked Bareos packages are available. Additional information can be found in the chapter Operating Systems.
If Bareos is available as a package, only 4 steps are required to get to a running Bareos system:
This will start a very basic Bareos installation which will regularly backup a directory to disk. In order to fit it to your needs, you’ll have to adapt the configuration and might want to backup other clients.
Decide about the Bareos release to use
There are different types of Bareos repositories:
Bareos Subscription repositories on https://download.bareos.com/
Contain the repositories for the Bareos Subscription customers.
The last three major releases are maintained, https://download.bareos.com/bareos/release/
Older versions stay available.
While the repository can be browsed, using them do require authentication credentials, which come with a Bareos subscription.
Bareos Community repositories on https://download.bareos.org/ with
latest build of the most recent Bareos stable branch at https://download.bareos.org/current/
latest build of the Bareos master branch at https://download.bareos.org/next/
For details, see Bareos Binary Release Policy.
The public key to verify a repository is also in repository directory (Release.key for Debian based distributions, repodata/repomd.xml.key for RPM based distributions).
The following code snippets are shell scripts that can be used as orientation how to download the package repositories and install Bareos packages. The release version number for bareos and the corresponding Linux distribution have to be updated for your needs, respectively.
To simplify the installation, all Linux and FreeBSD repositories on https://download.bareos.org/ and https://download.bareos.com/ contain a script named add_bareos_repositories.sh.
Download the add_bareos_repositories.sh script
matching the requested Bareos release
and the distribution of the target system.
Copy the script onto the target system and
execute it with a shell (sh) as root (e.g. using sudo)
or manually perform the steps that are documented in the script.
For example the script URL Debian 11 of the community current repository is:
For Bareos Subscription customers the URL of the bareos-22 release for Debian 11 is:
https://download.bareos.com/bareos/release/22/Debian_11/add_bareos_repositories.sh
Note
Bareos Subscription customers have credentials to authenticate against https://download.bareos.com. Some files can be accessed without authentication, but to use the repositories, authentication is mandatory. When downloading the file
add_bareos_repositories.sh, it is ready to use, because it contains your personal authentication credentials. Therefore downloading this file requires authentication. If this is inconvenient, you can alternatively downloadadd_bareos_repository_template.shand setBAREOS_USERNAMEandBAREOS_PASSWORDmanually.
Install the Bareos Software Packages
The Bareos Director requires a PostgreSQL database as its catalog. The Bareos database packages have their dependencies only to the database client packages, therefore the database itself must be installed manually.
Important
Install and start a PostgreSQL database server.
The package bareos is only a meta package which contains dependencies on the main components of Bareos, see Bareos Packages. If you want to setup a distributed environment (like one Bareos Director, separate database server, multiple Bareos Storage Daemons) you have to choose the regarding Bareos packages to install on each of the hosts instead of just installing the bareos package.
Install on RedHat based Linux Distributions
RHEL and derivatives, Fedora
Bareos Version >= 15.2.0 requires the Jansson library package. On RHEL 7 it is available through the RHEL Server Optional channel.
The RHEL_* repository is for Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the EL_* repositories are for RHEL derivatives, like AlmaLinux, CentOS Stream, Oracle and Rocky Linux. These repositories are automatically tested against several of this distributions.
Download the matching add_bareos_repositories.sh script from
https://download.bareos.com/bareos/release/,
https://download.bareos.org/current/ or https://download.bareos.com/next/,
copy it to the target system and execute it:
root@host:~# sh ./add_bareos_repositories.sh
root@host:~# yum install bareos
If authentication credentials are required (https://download.bareos.com)
they are stored within the repo file /etc/yum.repos.d/bareos.repo.
Install on SUSE based Linux Distributions
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES), openSUSE
Download the matching add_bareos_repositories.sh script from
https://download.bareos.com/bareos/release/,
https://download.bareos.org/current/ or https://download.bareos.com/next/,
copy it to the target system and execute it:
root@host:~# sh ./add_bareos_repositories.sh
root@host:~# zypper install bareos
If authentication credentials are required (https://download.bareos.com)
they are stored in the file /etc/zypp/credentials.d/bareos.
Install on Debian based Linux Distributions
Debian / Ubuntu / Univention Corporate Server (UCS)
Download the matching add_bareos_repositories.sh script from
https://download.bareos.com/bareos/release/,
https://download.bareos.org/current/ or https://download.bareos.com/next/,
copy it to the target system and execute it:
root@host:~# sh ./add_bareos_repositories.sh
root@host:~# apt update
root@host:~# apt install bareos
The add_bareos_repositories.sh script will:
Create a Bareos signature key file
/etc/apt/keyrings/bareos-*.gpg.Create the Bareos repository configuration file
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/bareos.sourcesThis file refers to the Bareos repository on the download server and to the local
/etc/apt/keyrings/bareos-*.gpgfile.
If authentication credentials are required (https://download.bareos.com) they are stored in the file
/etc/apt/auth.conf.d/download_bareos_com.conf.
Univention Corporate Server
The Univention Corporate Server (UCS) is an enterprise Linux distribution based on Debian.
Earlier releases (Bareos < 21, UCS < 5.0) offered extended integration into UCS and provided its software also via the Univention App Center. With version 5.0 of the UCS App Center the method of integration changed requiring commercially not reasonable efforts for deep integration.
Bareos continues to support UCS with the same functionality as the other Linux distributions.
During the build process, Bareos Debian 10 packages are automatically tested on an UCS 5.0 system. Only packages that passes this acceptance test, will get released by the Bareos project.
Note
While Bareos offers a software repository for UCS >= 5, this repository is identical with the corresponding Debian repository. The included APT sources file will also refer to the Debian repository.
Install on FreeBSD based Distributions
Download the matching add_bareos_repositories.sh script from
https://download.bareos.com/bareos/release/,
https://download.bareos.org/current/ or https://download.bareos.com/next/,
copy it to the target system and execute it:
root@host:~# sh ./add_bareos_repositories.sh
## install Bareos packages
root@host:~# pkg install --yes bareos.com-director bareos.com-storage bareos.com-filedaemon bareos.com-database-postgresql bareos.com-bconsole
The add_bareos_repositories.sh script will:
Create the Bareos repository configuration file
/usr/local/etc/pkg/repos/bareos.conf.If authentication credentials are required (https://download.bareos.com) they are stored inside the Bareos repository configuration file.
Prepare Bareos database
We assume that you already have your PostgreSQL database server installed and basically running.
For details, see chapter Catalog Maintenance.
Debian based Linux Distributions
Since Bareos Version >= 14.2.0 the Debian (and Ubuntu) based packages support the dbconfig-common mechanism to create and update the Bareos database.
Follow the instructions during install to configure it according to your needs.
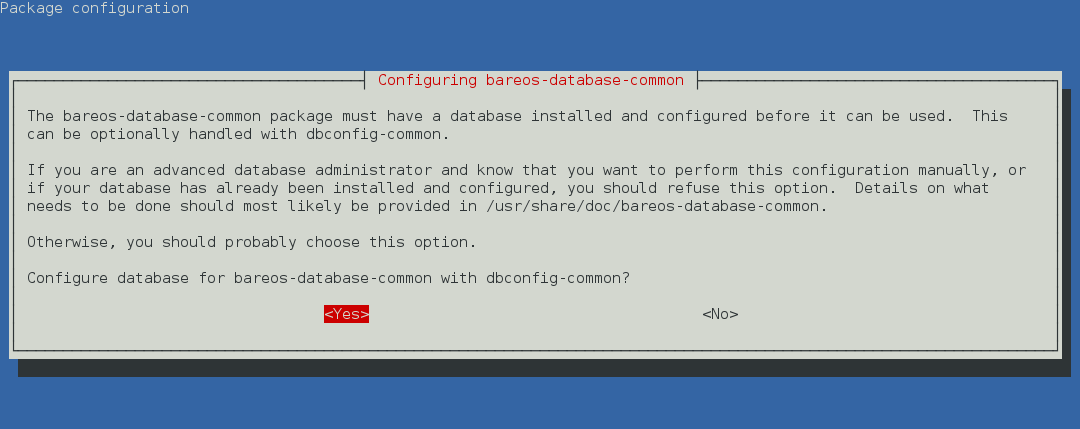
If you decide not to use dbconfig-common (selecting <No> on the initial dialog), follow the instructions for Other Platforms.
For details see dbconfig-common (Debian).
Other Platforms
If your PostgreSQL administration user is postgres (default), use the following commands:
su postgres -c /usr/lib/bareos/scripts/create_bareos_database
su postgres -c /usr/lib/bareos/scripts/make_bareos_tables
su postgres -c /usr/lib/bareos/scripts/grant_bareos_privileges
Start the daemons
Please remark, the Bareos Daemons need to have access to the TCP ports 9101-9103.
Linux
Depending on the Linux distribution, the name of the Bareos services either correspond to the package names (Debian and derivatives) or to the binary names (e.g. RPM based distributions).
To enable and start the daemon, either use
root@host:~# systemctl enable --now bareos-director.service
root@host:~# systemctl enable --now bareos-storage.service
root@host:~# systemctl enable --now bareos-filedamon.service
or
root@host:~# systemctl enable --now bareos-dir.service
root@host:~# systemctl enable --now bareos-sd.service
root@host:~# systemctl enable --now bareos-fd.service
FreeBSD
## enable services
root@host:~# sysrc bareosdir_enable=YES
root@host:~# sysrc bareossd_enable=YES
root@host:~# sysrc bareosfd_enable=YES
## start services
root@host:~# service bareos-dir start
root@host:~# service bareos-sd start
root@host:~# service bareos-fd start
Now you should be able to log in to the Bareos Director using the Bareos Console.
When you want to use the Bareos WebUI, please refer to the chapter Installation.